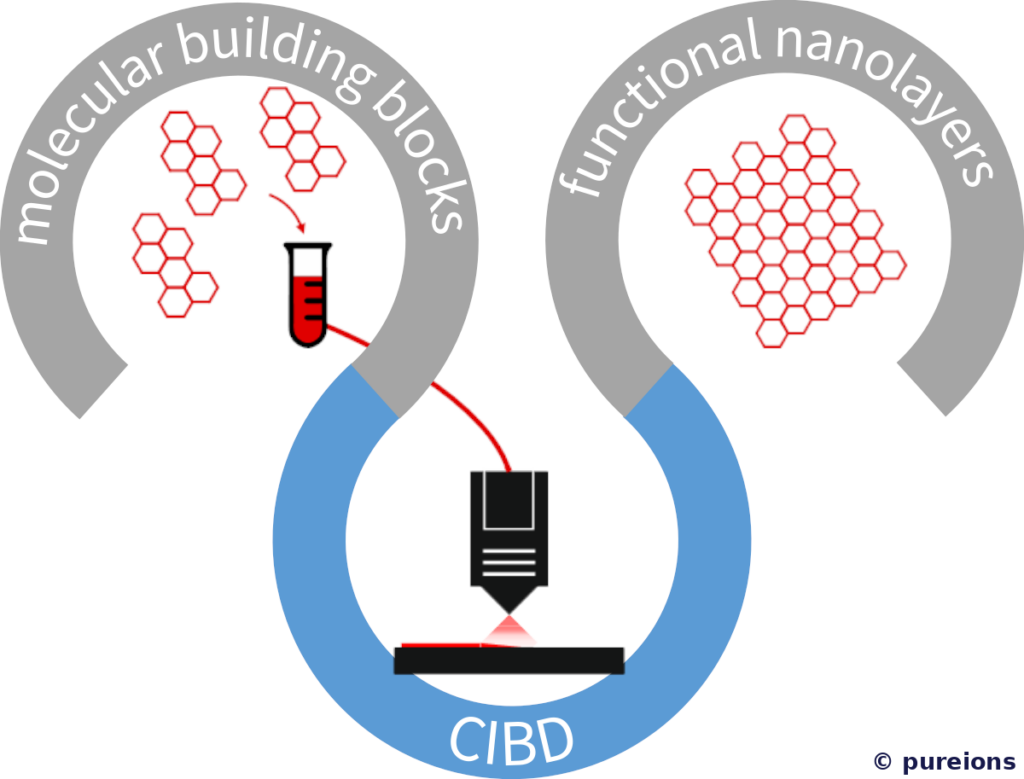
CIBD
Controlled Ion-Beam Deposition (CIBD) is a technology that allows the deposition of organic monolayers on surfaces.
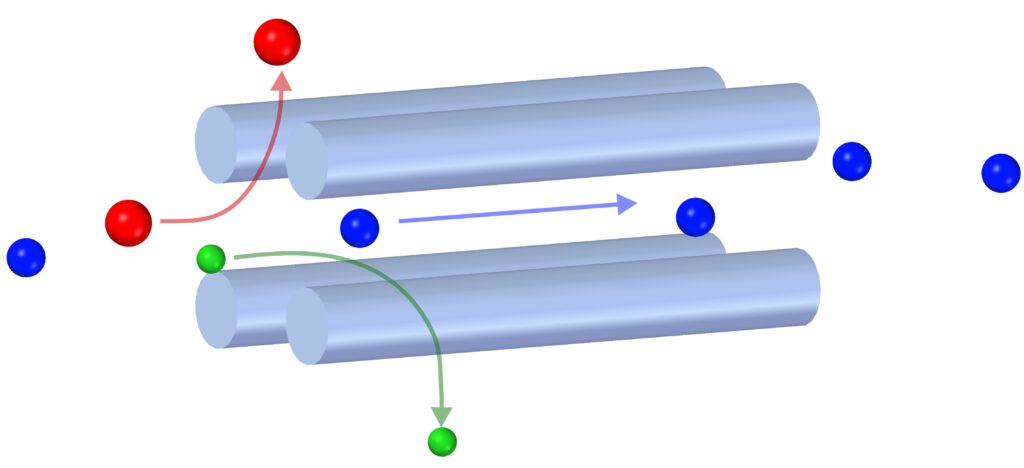
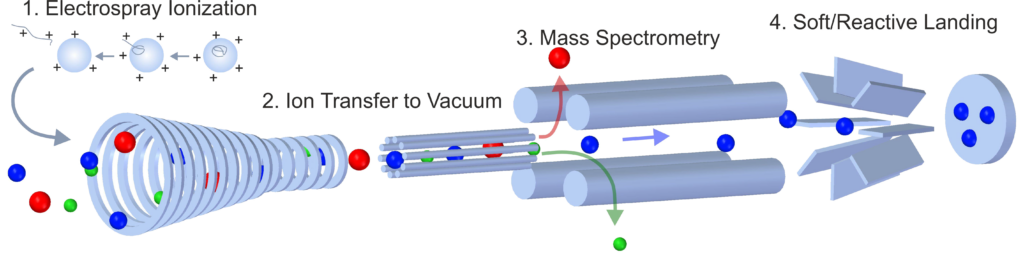
- The ions typically originate from an electrospray ionization (ESI) source, a cluster source, matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI), or from molecules gathered from a surface under ambient conditions by desorption ESI (DESI).
- The ions are guided through differentially pumped vacuum stages using ionguides.
- In vacuum, a digital Quadrupole Mass Filter (dQMF) is used to analyze and filter the ions.
- Finally, the ions are landed on the target surface. The landing energy can be chosen freely to facilitate soft and/or reactive landing.
Key advantages over existing technologies:
- Mass-selected deposition of a wide range of molecule types
- virtually unlimited mass range via digital RF ion guides and a digital Quadrupole Mass Filter (dQMF)
- High yields and transmission efficiencies
- High yields and transmission efficiencies
- Exact dose control via landed charge
- Precise control of landing energy
- Beam current monitoring in every stage
- Gate valve interlock to prevent ventilation
- Zero vibrations during standby
- Ion-source quickly exchangeable
- Modular component design for future updates and extensions
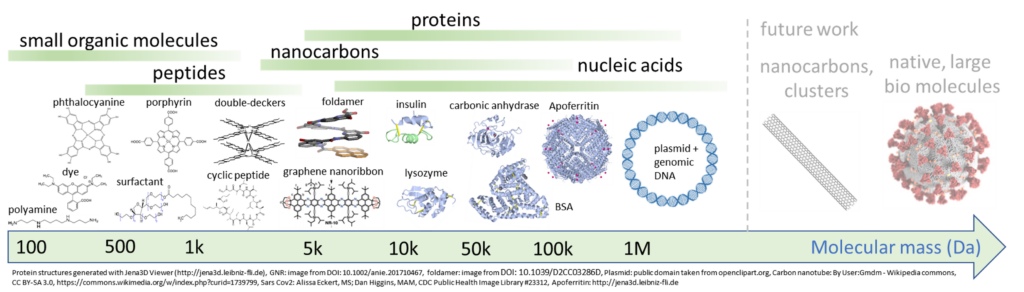
Molecules
Due to our digital Quadrupole Mass Filter (dQMF), there is virtually no limit to the mass of usable molucules. An selection of already processed molecules is displayed here:
dQMF
Unlike every commercial Quadrupole Mass Filter (QMF) known to us, our dQMF does not operate with a resonantly generated sine-shaped voltage but in a“digital”mode. The RF signal is a computer-controlled square wave with steadily variable frequency and amplitude. Due to the tunable frequency, whichis adapted to the mass of the molecules under investigation, the optimum RF parameters for each molecule can be chosen. There is virtually no limit for the accessible m/z range of the transmitted molecules. To our knowledge, this flexibility is currently not achieved by any other QMF. The dQMF accomplishes both tasks of the CIBD system – the analysis of the ion beam and the selection of distinct species during deposition.